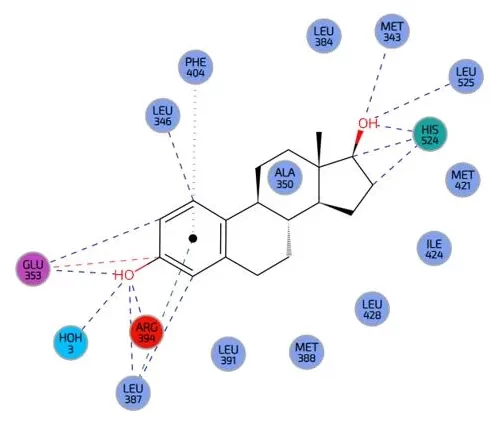
Molecular docking, virtual docking, homology modelling, virtual complexation experiments
This is a computational technique used to predict how small molecules (ligands) interact with a target protein, aiding in drug discovery, designing host – guest chemistries and predicting complexation for example of metal ions.
Virtual docking simulates ligand binding within the active site or cavity, assessing binding affinity and stability. Homology modeling predicts protein structures when experimental data is unavailable, enabling docking studies. Virtual complexation experiments analyze protein-ligand interactions in silico to optimize drug design.
Use of Virtual headsets to get “inside” protein ligand complexes to gain unique perspectives
Emerging technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) headsets, allow researchers to visualize and manipulate protein-ligand complexes in 3D, providing unique insights into binding interactions, structural flexibility, and drug optimization, enhancing rational drug design strategies.
Biomimetic experiments
Virtual studies especially the use of halogens such as chlorine and fluorine to change not only lipid solubility and steric bulkheads but also in creating improved electrostatics and intermolecular bonding in improving host – guest, cavity and protein – ligand interactions.
We also offer bespoke generation of molecular docking images for use in art work and associated media.